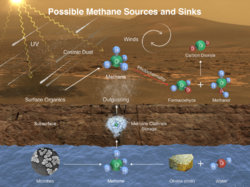
NASA's Mars Curiosity rover has measured a tenfold spike in methane, an organic chemical, in the atmosphere around it and detected other organic molecules in a rock-powder sample collected by the robotic laboratory’s drill.
"This temporary increase in methane -- sharply up and then back down -- tells us there must be some relatively localized source," said Sushil Atreya of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Curiosity rover science team. "There are many possible sources, biological or non-biological, such as interaction of water and rock."
Researchers used Curiosity’s onboard Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) laboratory a dozen times in a 20-month period to sniff methane in the atmosphere. During two of those months, in late 2013 and early 2014, four measurements averaged seven parts per billion. Before and after that, readings averaged only one-tenth that level.
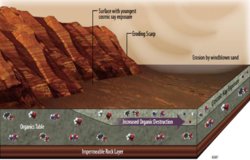
Curiosity also detected different Martian organic chemicals in powder drilled from a rock dubbed Cumberland, the first definitive detection of organics in surface materials of Mars. These Martian organics could either have formed on Mars or been delivered to Mars by meteorites.
Organic molecules, which contain carbon and usually hydrogen, are chemical building blocks of life, although they can exist without the presence of life. Curiosity's findings from analyzing samples of atmosphere and rock powder do not reveal whether Mars has ever harbored living microbes, but the findings do shed light on a chemically active modern Mars and on favorable conditions for life on ancient Mars.
Researchers worked many months to determine whether any of the organic material detected in the Cumberland sample was truly Martian. Curiosity’s SAM lab detected in several samples some organic carbon compounds that were, in fact, transported from Earth inside the rover. However, extensive testing and analysis yielded confidence in the detection of Martian organics.
Identifying which specific Martian organics are in the rock is complicated by the presence of perchlorate minerals in Martian rocks and soils. When heated inside SAM, the perchlorates alter the structures of the organic compounds, so the identities of the Martian organics in the rock remain uncertain.
"This first confirmation of organic carbon in a rock on Mars holds much promise," said Curiosity participating scientist Roger Summons of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. "Organics are important because they can tell us about the chemical pathways by which they were formed and preserved. In turn, this is informative about Earth-Mars differences and whether or not particular environments represented by Gale Crater sedimentary rocks were more or less favorable for accumulation of organic materials. The challenge now is to find other rocks on Mount Sharp that might have different and more extensive inventories of organic compounds."
Researchers also reported that Curiosity's taste of Martian water, bound into lakebed minerals in the Cumberland rock more than three billion years ago, indicates the planet lost much of its water before that lakebed formed and continued to lose large amounts after.
SAM analyzed hydrogen isotopes from water molecules that had been locked inside a rock sample for billions of years and were freed when SAM heated it, yielding information about the history of Martian water. The ratio of a heavier hydrogen isotope, deuterium, to the most common hydrogen isotope can provide a signature for comparison across different stages of a planet's history.
"It's really interesting that our measurements from Curiosity of gases extracted from ancient rocks can tell us about loss of water from Mars," said Paul Mahaffy, SAM principal investigator of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and lead author of a report published online this week by the journal Science
The ratio of deuterium to hydrogen has changed because the lighter hydrogen escapes from the upper atmosphere of Mars much more readily than heavier deuterium. In order to go back in time and see how the deuterium-to-hydrogen ratio in Martian water changed over time, researchers can look at the ratio in water in the current atmosphere and water trapped in rocks at different times in the planet’s history.
Martian meteorites found on Earth also provide some information, but this record has gaps. No known Martian meteorites are even close to the same age as the rock studied on Mars, which formed about 3.9 billion to 4.6 billion years ago, according to Curiosity’s measurements.
The ratio that Curiosity found in the Cumberland sample is about one-half the ratio in water vapor in today's Martian atmosphere, suggesting much of the planet's water loss occurred since that rock formed. However, the measured ratio is about three times higher than the ratio in the original water supply of Mars, based on assumption that supply had a ratio similar to that measured in Earth's oceans. This suggests much of Mars' original water was lost before the rock formed.
The results of the Curiosity rover investigation into methane detection and the Martian organics in an ancient rock were discussed at a news briefing Tuesday at the American Geophysical Union's convention in San Francisco. The methane results are described in a paper published online this week in the journal Science by NASA scientist Chris Webster of JPL, and co-authors.
A report on organics detection in the Cumberland rock by NASA scientist Caroline Freissenet, of Goddard, and co-authors, is pending publication.